Working Principle
Insect traps are used for trapping harmful nocturnal pests in agriculture and horticulture crops. Solar insect trap devices use a different type of lights, like, UV, yellow, mercury to attract pest toward light sources, UV light is one of the most effective types of light for attracting pest toward it.
Hectare solar insect trap is also based on UV light. Insect files toward the light source and hits its flaps and fall in water tub beneath it. Water tub is filled with water, which makes it difficult for insects to fly back. Any agent, like detergent, shampoo or kerosene can be added in water tub to reduce the surface tension of water.
How it works
Solar insect trap contains solar panel , battery, light and circuit for automation, water tub and stand.
Solar panel charges the battery during the daytime. Its software allows solar trap to start automatically after sunset and regulate the timing of solar trap.
Where it is useful
Solar trap is useful for control of nocturnal pest. There is different type of traps which are used against different pest, so it is very important for farmers to know which pest are attacking the crop and which traps are going to most beneficial.
Solar trap is effective against the nocturnal pest, which flies during the night-time. Below is the brief list of pest where solar trap being useful. We have tried our best to compile the list, still it is not complete list and solar trap is effective against other pests also. You find in page or CTRL+F to find details of particular crops or pest.
| CROP |
PEST |
Symptoms |
|
|
| Rice |
Leaf hoppers (Nephotettix virescens) |
Hopper burn |
 |
 |
| Rice |
Brown plant leafhopper: Nilaparvata lugens |
Circular patches of drying or Hopper burn |
 |
 |
| Rice, sorghum, Mazie |
Chilo suppressalis |
Dead heart during vegetative stage and white ear during reproductive stage |
 |
 |
| Maize |
Leafhopper: Pyrilla perpusilla |
Yellow leaves covered with black sooty Mould |
 |
 |
| Finger millet |
Leaf folder: Nephrosclerosis medinalis |
Leaf folding and scrapping |
 |
 |
| Redgram, green gram, black gram, cowpea |
Grass blue butterfly: Euchrysops cnejus |
Hole in the pod |
 |
 |
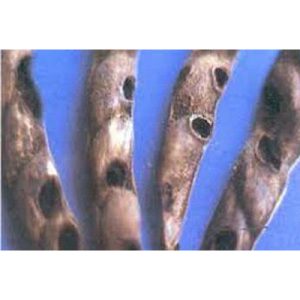
| Redgram |
Field bean pod borer: Adisura atkinsoni |
The larva bores inside the pod and feeds on the seeds within. |
 |
 |
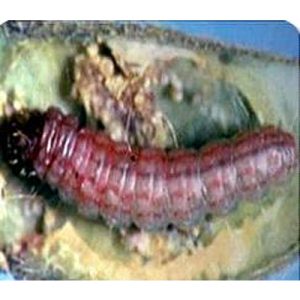
| Green gram, black gram |
Spiny pod borer: Etiella zinckenella |
Dropping of flowers |
 |
 |
| Bengal gram |
Semilooper : Autographa nigrisigna |
Skeletonization of leaves and the plant becomes whitish |
 |
 |
| Soybean |
Bihar hairy caterpillar: Spilosoma obliqua |
Net or web appearance on leaves
And defoliation |
 |
 |
| Ground nut, Castor |
Red Hairy caterpillars: Amsacta albistriga, A. moorei |
Defoliation |
 |
 |
| Sugarcane |
White Grub: Holotrichia consanguinea |
Yellowing and wilting |
 |
 |
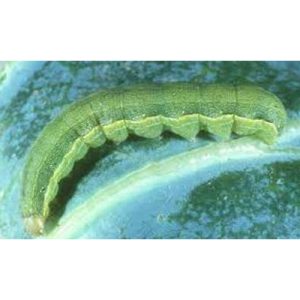
| Vegetable |
Beat armyworm
Spodoptera exigua (Hübner) |
Circular and irregulated holes |
 |
 |
| Vegetables |
Oriental tobacco budworm |
Chewing holes at the base of fruits |
 |
 |
| Cabbage |
Diamond black moth |
White patches on leaves and defoliation |
 |
 |
| Peach, apricot, plum, apple, pear |
Peach Carposinidae |
Small holes on the surface of fruit |
 |
 |
| Peach, apricot, plum, apple, pear |
Peach oriental fruit moth |
gumming with brown sawdust-like frass. |
 |
 |
| Peach, cherry, apple, plum, mandarin, chestnut, corn, cotton, sunflower |
Peach pyralid moth |
Damage on fruit |
 |
 |
| Tomato, cotton, maize, Bhindi, Chilli, Sorghum, Maize, red gram, green gram, black gram, Bengal gram, cowpea, Soybean, Sunflower, groundnut |
Fruit borer (Helicoverpa armigera) |
Circular holes on fruit |
 |
 |
| Tomato, Chilli, Banana, soybean, Sunflower, ground nut, Castor, cotton |
Lead eating caterpillar (Spodoptera litura) |
Scrapping of leaves on ventral surface and defoliation |
 |
 |
| Tomato |
Pinworm: Tuta absoluta |
Pinhole in fruit |
 |
 |
| Brinjal |
Fruit borer (Leucinodes orbonalis) |
Withering of terminal shoots/dead hearts
Bore holes on shoots and fruits plugged with excreta
Shedding of flower buds
Withering and drying of leave |
 |
 |
| Brinjal |
Stem borer (Euzophera perticella) |
Top shoots of young plants droop and wither.
Older plants become stunted.
Fruit bearing is affected |
 |
 |
| Cabbage |
Cutworm (Trichoplusia ni) |
Small irregular holes on leaves |
 |
 |
| Onion |
Cutworm (Agrotis ipsilon) |
Young larva feeds on tender foliage and grown-up larva cuts the stem at collar region. |
 |
 |
| Mango |
Loopers (Thalassodes quadrari) |
Presence of gallery made out of silk and frass on trunk. |
 |
 |
| Mango |
Shoot borer hairy caterpiller (Euproctis fraterna, Prothesia scintillans) |
Defoliation |
 |
 |
| Guava, Pomegranate, Turmeric , Ginger |
Fruit borer (Dichocrocis punctiferalis) |
Caterpillar bores into young fruits
Feeds on internal contents (pulp and seeds)
Dry up and fall off in without ripening |
 |
 |
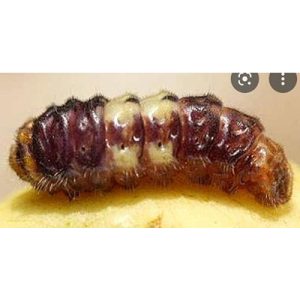
| Guava, Pomegranate, Amla |
Fruit borers: Deudorix (Virachola) isocrates
|
Caterpillar bores into young fruits
Feeds on internal contents (pulp and seeds) |
 |
 |
| Guava |
Fruit borer: Rapala varuna
|
Caterpillar found on flower buds and fruit |
 |
 |
| Banana |
Castor hairy caterpillar: Pericallia ricini |
Caterpillar scraping the chlorophyll content and windowing in unfurled leaves. |
 |
 |
| Citrus, Amla |
Fruit sucking moth: Otheris materna, O. ancilla, O. fullonica |
Adult pierce the fruit, sucks the juice causing rotting and dropping |
 |
 |
| Pine apple, Coconut |
Rhinoceros beetle: Oryctes rhinoceros |
Wilting of the plant due to adult boring at the base of the stem. |
 |
 |
| Caramom |
Hairy caterpillars: Eupterote cardamomi, E. canarica, E. fabia |
Plant defoliation |
 |
 |
| Coconut |
Slug Caterpillar: Parasa lepida and Contheyla rotunda |
Defoliated palm |
 |
 |
| Coconut |
Coreid Bug: Paradasynus rostratus |
Deformed fruits |
 |
 |
| Coconut |
Bag Worm: Manatha albipes |
Small and irregular hole on the leaves. Silken spin stick strand bags below the leaf |
 |
 |
| Coconut |
White Grub/ Cockchafer Beetle: Leucopholis coneophora |
yellowing of leaves, premature nut shedding, delayed flowering, retardation in growth and yield decline. |
 |
 |
| Coffee |
Cockchafers or white grubs: Holotrichia spp. |
Yellowing, stunt growth and wilting |
 |
 |
FAQ
1) What are the other expenses of using solar insect trap?
It is a product which does not have any other expenses once you purchase it. You need to change its water every 2-3 days, rest leave all to solar trap.
2) Caterpillars do damage, how it is effective against them?
Caterpillars born from egg laid by moth / flying pest. As it traps the flying pest, it will break the life cycle of pest. The more the number of pest solar trap killed, less the number of pests remain alive in your field to lay eggs and lesser will be caterpillars.
3) Do I still need to spray pesticide after using solar insect trap?
a. It depends on crop to crop. As the solar trap is effective against some genera of insect, you may still need to use insecticide or other type of traps for complete control, like solar trap is not used for fruit fly, you need to use pheromone based fly trap, it is not effective against mealy bugs/ aphids/ jassids, if your field is infected with these pest also, you may need to spray pesticide or take recommended measures to control these pest.
4) What is the life of solar trap?
a. Solar traps have long life. Its solar panel have life of 25 years, whereas its light and battery have life of 3 years, based on the use, you may need to change its battery of light, we have all the spares available, and you can contact us to purchase spare parts.
5) Do I need to switch it on daily?
a. No, it is completely automatic, once you install in field, switch it on and leave it. After that it will on and off based on time and work automatically, you only need to switch it off when you want to keep it at home during off-season
6) Can I use it in home also?
a. No, it is only for agriculture use. Please do not install it at home
7) How many solar traps are required for my field?
a. It has coverage area of 2 acer ( 50 m radius). Based on your field size and shape you can stall.
8) It has height adjustment, what is the use of that?
a. Solar trap needs to install at 1 feet above the canopy, you need to increase its height as crop height increases. For fruit crop install it in open space.
9) Does it trap honeybees or any beneficial insect?
a. It does not trap beneficial pest, as it works during the time when the harmful pest is active. Honeybees are not nocturnal insects.














































































